These options diversification strategies will help you limit your exposure to risk and overcome the fear of loss. This hands-on guide will share a powerful example of an optional box distribution strategy. We cover the basics of bull call spread strategy to help you hedge risk and increase your chance of profit.
If this is your first time on our site, our team at Trading Strategy Guides welcomes you. Be sure to click the subscribe button so you get your free trading strategy delivered straight to your inbox every week.
With tradable options, it is important to understand the math behind them. The biggest “AHA!” a moment in your options career will be when you understand how option spreads work. Options spread trading strategies provide an excellent opportunity to improve your profits. Start by reading our Option Spread Strategies PDF.
Unlock options traded on Robinhood App and start buying options that are cheaper and commission-free with the help of: Robinhood App Trading Guide (Everything You Need to Know). This is one of the easiest places to trade free options.
We are going to outline the introduction to spreading options and describe how to become a successful options trader.
What is an option spread? How do options spreads work?

Trading spread options is the act of buying and selling the same type of option simultaneously. There are two types of options: Call Options and Put Options. Call options give you the right to buy in the future. Put options give you the right to sell in the future. For example, if you buy a call option on Amazon stock and simultaneously sell another option on Amazon stock, you have opened a spread trading position.
Usually, spreads are composed of at least two-leg order or a multi-leg option order such as the butterfly spread option strategy.
Options spreads can be confusing, but it is easy to understand if you read the complete guide to options trading, which can be found here: Call Option vs Put Option – Introduction to Options Trading.
The difference in either the expiration dates or the strike prices between the two options is called the spread.
The most important takeaway when building a distribution:
- The combination of options is based on the same underlying asset. For example, if you buy calls for Apple stock, you are also selling calls for the same stock Apple.
- You must buy and sell the same type of option. For example, if you buy a call option, you are selling another call option
- You can use a variety of combinations of expiration dates and / or strike prices.
Let’s see what are the simplest combinations to form a spread:
What is a call spread option strategy?
A call spread is an option strategy used when you believe the underlying asset price will rise. The call spread strategy involves buying an at-the-money call option and selling an at-the-money call option (higher strike price). Both options have the same expiration date.
The call spread is also known as the bull call spread strategy. Participate in this strategy when markets look bearish.
The spread options will help you to profit in any kind of market conditions. You can tackle bullish trends and bearish trends.
For bearish trends, we use the bear call spread strategy. Use this strategy if it appears that prices are likely to fall. The bear call spread is an option strategy that involves buying and at-the-money call options and selling an at-the-money option call (lower strike price). Both options have the same expiration date.
The carry call spread strategy is also known as the short call spread.
But what if we are stuck in a market bound market?
Spread options are the most versatile financial instruments. With the right options trading strategy, your portfolio can become significantly more diverse and dynamic. You have endless strike prices and expiration dates at your disposal, so you can set up a complicated calendar spread strategy. The spread of options can therefore be adjusted based on the current market conditions, including sideways trading.
Distribution options are a double-edged sword. On the one hand, you limit the risk, but on the other hand, the potential profits are also limited. The spread of options will always create a limited price range from which you can profit.
Further information on the different types of lubricants is presented below:
Types of options distributed:
In this segment, we are going to break down how many types of options are spread and help you better understand these concepts. Option spreads can be divided into three main categories:
- Vertical distribution option trading strategy.
- Horizontal spread option strategy.
- Diagonal spread option strategy.
1. Strategy for vertical distribution
Vertical spreadsheets are constructed using simple option spreads. A vertical spread is an option strategy that requires:
- Buy and put options of the same type (calls or puts).
- Same expiration date.
- Same underlying asset.
- But different strike prices.
On the options chain, these positions appear vertically stacked, hence the name vertical spread.
We can distinguish four types of strategies for vertical distribution options:
- Bull Call Spread Option Strategy
- Carry call spread option strategy
- Bull Put Spread Option Strategy
- Bear Put spread option strategy
We are going to discuss the spread of the bull call because all others are based on the same technique and function. We can also go a step further and spread according to the capital layout (debit spread or credit spread):
- Debit spread strategy occurs when you incur an upfront cost for purchasing the options.
- Trade strategy for credit spread options occurs when you receive credit in advance from the purchase of the options.
2. Horizontal Distribution Option Strategy
A horizontal spread is an option strategy that requires:
- Buy and put options of the same type (calls or puts).
- Same strike price.
- Same underlying asset.
- But different expiration dates.
Horizontal spreads are also commonly known as calendar spread or time spread because we have different expiration dates.
3. Diagonal Spread Option Strategy
A diagonal spread is an option strategy that requires:
- Buy and put options of the same type (calls or puts).
- Same underlying asset.
- But different expiration dates.
- And different strike prices.
Horizontal spreads and diagonal spreads are both examples of calendar spreads. The calendar option spread is an advanced strategy that takes advantage of both the decay in the option prices and the difference between the contract months and the downward directional movement of the underlying stock. As the price changes over time, you get many opportunities for profit.
Check out our example of the diagonal spread option strategy HERE.
The most important point is that you should be familiar with all types of options that are distributed. This will increase your chance of success.
Bull Call Spread Option Strategy
What is a bull call spread?
Spreading a bull call requires simultaneously buying at-the-money calls and then selling at-the-money calls with the same expiration dates. The reason we sell ATM calls (out of the money) is to help fund the ATM calls (at the money). We know that ATM calls can be quite expensive, so this is a great method to reduce the cost along with the premium price for options.
In options trading, premiums are prepaid fees you pay when you buy a call option. If you sell a call option, the investor receives the premium. So, by selling the second ATM call option, you basically recoup the prices you paid for the first ATM call option.
Premiums can be very expensive if the price of the option strike is close to the current stock price.
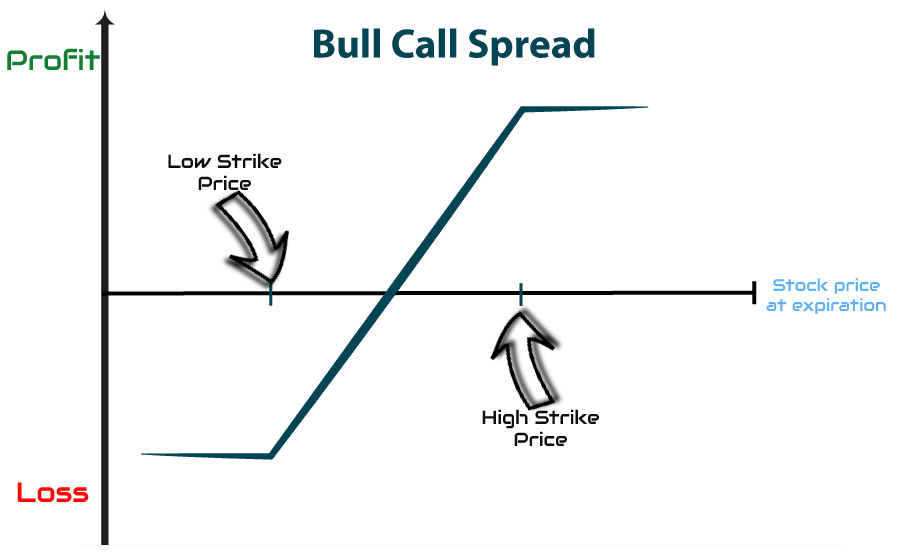
How can you profit from spreading bull calls?
As the name suggests (BULL call), you benefit from a bull call spread if the underlying asset will increase in value. The market sentiment should go higher.
Bull + Call = Bull represents a market going higher + Call is an option you buy if you think the market is going to go higher.
The most important element of the bull call spread is the assumption that the market price will rise.
What is the maximum risk associated with spreading bull calls?
The maximum loss you can suffer with a bull call spread is the premium price you pay for the option plus the fees. The potential loss will always be known before trading.
What is the maximum profit you can earn from the call spread trading strategy?
The profit can be calculated by taking the difference of the strike prices (ATM call and ATM call) minus the maximum risk, which we calculated previously.
Call spread option profit = Strike prices – Maximum risk
Let’s look at a quick example so we can apply the theory of options trading.
For this example, we’ll go with Apple’s pricing options.
At the time of writing this Options Spread Strategy PDF, Apple’s stock price is trading around 3 per share.
The first step to setting up your bull call spread is to buy ATM calls at 3. Second, because we assume that the APPL stock price will go higher, we sell ATM calls at 250 dollars. Our winnings will be capped at 0.
For simplicity, let’s assume you pay
The ultimate cost of
The right way to buy cheap options is to use the call spread strategy. However, this strategy for trading options is more suitable if you think that the underlying asset will rise only moderately.
In the next segment, we take a box spread strategy and construct a practical example that leads to a risk-free arbitrage opportunity.
Example of a strategy for box distribution (long box)

The box spread is a complicated arbitrage strategy that takes advantage of the price efficiency in option pricing. When the spread options are underpriced relative to their expiration date, a risk-free arbitrage trading opportunity is created.
The strategy for spreading the box is also known as the long box strategy.
Setting up options for the spread of a box involves putting together a strategy for trading with four legs or the combination of two vertical spreads as follows:
- Buy a bull call spread option (1 ITM call and 1 ATM call).
- Buy a bear spread option (1 ITM put and 1 ATM put).
The strategy for the short-case options is opposite to the long-case strategy.
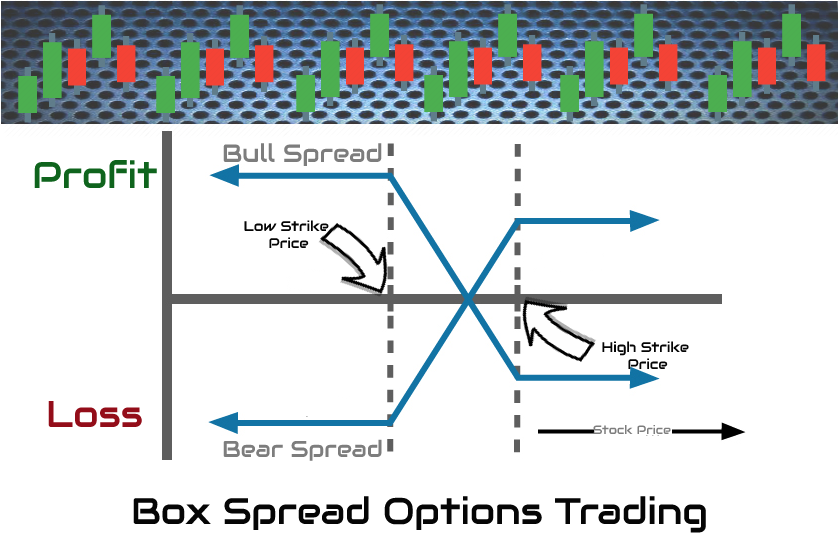
The way you take advantage of the box spread options and create a risk-free position is by using the same expiration dates and strike prices for the vertical spread. While we eliminate the risk, the distribution of the box also has the disadvantage of only providing a small return.
Example of a box spread
Let’s take a simple example of the Alibaba indicator symbol BABA trading at 0. The following option premium prices are available:
- October 175 call –
- October 185 call –
- October 175 put – $ 50
- October 185 put – $ 5
To execute a subject spread, the investor must buy both vertical spreads:
- Buy Bull Call Spread = Buy October 175 call + Sell October 185 call = ( x 0 contract size) – (x 0 contract size) = 0.
- Buy Bear Put Spread = Buy October 175 put + Sell October 185 put = (
.5 x 100 contract size) – ( x 0 contract size) = 0.Not including commissions, the total cost of opening the subject spread is 0 + 0 = 0.
The maturity value of the distribution of the strike price is: $ 185 – $ 175 = $ 10 x $ 100 shares = $ 1,000.
The total profit without including the option fee is calculated as follows:
,000 – 0 = 0.admin2023-02-08T20:56:32+00:00If you use the wrong Options broker, the potential profits generated by the subject spread can be offset by the large commissions. Be sure to invest in options using Robinhood, the commission-free platform.
When Should You Use the Butterfly Spread Option Strategy?

The butterfly spread is a neutral trading strategy that can be used if you expect low volatility in the underlying asset. The butterfly spread uses a combination of a bull spread and a bear spread, but with only three legs. If you are trying to go long, the three-leg option strategy can be constructed as follows:
- Buy in-the-money call
- Sell two at-the-money calls
- Buy one call without money
The butterfly risk for long calls is limited to the premium cost you pay for opening the tripod positions. The butterfly can also be constructed by combining and selling a belt and buying a choke.
Learn the art of trading the straddle option spread strategy to take the next big step: Straddle Option Strategy – Profit from Big Moves.
The short butterfly strategy is the reverse strategy for the long butterfly.
Final words – options distribution strategies
While stock traders need to be 100% right in order to make a profit, the options spread strategies can make you money even if you are only partially right about your trades. Option spreads can help you develop non-directional trading strategies, such as the example of the option spread option strategy outlined in this course on options spreads.
Many options traders begin their career by simply buying puts or calls. But at some point along with the evolution of an options trader, they quickly move to spread trading options. For example, implementing a strategy for spreading bull call options gives you better risk control.
For more options trading tricks and strategies follow: Top 10 Options Blogs and Websites to Follow in 2019.
Do not forget that trading in spread options exists with many alternatives for managing risk. Nowadays, most options trading platforms make it easy to place complex options strategies at once. Try them on a demo options platform before risking your hard-earned money.
Thanks for reading!
- Buy Bear Put Spread = Buy October 175 put + Sell October 185 put = (
admin2023-02-08T20:56:32+00:00
These options diversification strategies will help you limit your exposure to risk and overcome the fear of loss. This hands-on guide will share a powerful example of an optional box distribution strategy. We cover the basics of bull call spread strategy to help you hedge risk and increase your chance of profit.
If this is your first time on our site, our team at Trading Strategy Guides welcomes you. Be sure to click the subscribe button so you get your free trading strategy delivered straight to your inbox every week.
With tradable options, it is important to understand the math behind them. The biggest “AHA!” a moment in your options career will be when you understand how option spreads work. Options spread trading strategies provide an excellent opportunity to improve your profits. Start by reading our Option Spread Strategies PDF.
Unlock options traded on Robinhood App and start buying options that are cheaper and commission-free with the help of: Robinhood App Trading Guide (Everything You Need to Know). This is one of the easiest places to trade free options.
We are going to outline the introduction to spreading options and describe how to become a successful options trader.
What is an option spread? How do options spreads work?

Trading spread options is the act of buying and selling the same type of option simultaneously. There are two types of options: Call Options and Put Options. Call options give you the right to buy in the future. Put options give you the right to sell in the future. For example, if you buy a call option on Amazon stock and simultaneously sell another option on Amazon stock, you have opened a spread trading position.
Usually, spreads are composed of at least two-leg order or a multi-leg option order such as the butterfly spread option strategy.
Options spreads can be confusing, but it is easy to understand if you read the complete guide to options trading, which can be found here: Call Option vs Put Option – Introduction to Options Trading.
The difference in either the expiration dates or the strike prices between the two options is called the spread.
The most important takeaway when building a distribution:
- The combination of options is based on the same underlying asset. For example, if you buy calls for Apple stock, you are also selling calls for the same stock Apple.
- You must buy and sell the same type of option. For example, if you buy a call option, you are selling another call option
- You can use a variety of combinations of expiration dates and / or strike prices.
Let’s see what are the simplest combinations to form a spread:
What is a call spread option strategy?
A call spread is an option strategy used when you believe the underlying asset price will rise. The call spread strategy involves buying an at-the-money call option and selling an at-the-money call option (higher strike price). Both options have the same expiration date.
The call spread is also known as the bull call spread strategy. Participate in this strategy when markets look bearish.
The spread options will help you to profit in any kind of market conditions. You can tackle bullish trends and bearish trends.
For bearish trends, we use the bear call spread strategy. Use this strategy if it appears that prices are likely to fall. The bear call spread is an option strategy that involves buying and at-the-money call options and selling an at-the-money option call (lower strike price). Both options have the same expiration date.
The carry call spread strategy is also known as the short call spread.
But what if we are stuck in a market bound market?
Spread options are the most versatile financial instruments. With the right options trading strategy, your portfolio can become significantly more diverse and dynamic. You have endless strike prices and expiration dates at your disposal, so you can set up a complicated calendar spread strategy. The spread of options can therefore be adjusted based on the current market conditions, including sideways trading.
Distribution options are a double-edged sword. On the one hand, you limit the risk, but on the other hand, the potential profits are also limited. The spread of options will always create a limited price range from which you can profit.
Further information on the different types of lubricants is presented below:
Types of options distributed:
In this segment, we are going to break down how many types of options are spread and help you better understand these concepts. Option spreads can be divided into three main categories:
- Vertical distribution option trading strategy.
- Horizontal spread option strategy.
- Diagonal spread option strategy.
1. Strategy for vertical distribution
Vertical spreadsheets are constructed using simple option spreads. A vertical spread is an option strategy that requires:
- Buy and put options of the same type (calls or puts).
- Same expiration date.
- Same underlying asset.
- But different strike prices.
On the options chain, these positions appear vertically stacked, hence the name vertical spread.
We can distinguish four types of strategies for vertical distribution options:
- Bull Call Spread Option Strategy
- Carry call spread option strategy
- Bull Put Spread Option Strategy
- Bear Put spread option strategy
We are going to discuss the spread of the bull call because all others are based on the same technique and function. We can also go a step further and spread according to the capital layout (debit spread or credit spread):
- Debit spread strategy occurs when you incur an upfront cost for purchasing the options.
- Trade strategy for credit spread options occurs when you receive credit in advance from the purchase of the options.
2. Horizontal Distribution Option Strategy
A horizontal spread is an option strategy that requires:
- Buy and put options of the same type (calls or puts).
- Same strike price.
- Same underlying asset.
- But different expiration dates.
Horizontal spreads are also commonly known as calendar spread or time spread because we have different expiration dates.
3. Diagonal Spread Option Strategy
A diagonal spread is an option strategy that requires:
- Buy and put options of the same type (calls or puts).
- Same underlying asset.
- But different expiration dates.
- And different strike prices.
Horizontal spreads and diagonal spreads are both examples of calendar spreads. The calendar option spread is an advanced strategy that takes advantage of both the decay in the option prices and the difference between the contract months and the downward directional movement of the underlying stock. As the price changes over time, you get many opportunities for profit.
Check out our example of the diagonal spread option strategy HERE.
The most important point is that you should be familiar with all types of options that are distributed. This will increase your chance of success.
Bull Call Spread Option Strategy
What is a bull call spread?
Spreading a bull call requires simultaneously buying at-the-money calls and then selling at-the-money calls with the same expiration dates. The reason we sell ATM calls (out of the money) is to help fund the ATM calls (at the money). We know that ATM calls can be quite expensive, so this is a great method to reduce the cost along with the premium price for options.
In options trading, premiums are prepaid fees you pay when you buy a call option. If you sell a call option, the investor receives the premium. So, by selling the second ATM call option, you basically recoup the prices you paid for the first ATM call option.
Premiums can be very expensive if the price of the option strike is close to the current stock price.

How can you profit from spreading bull calls?
As the name suggests (BULL call), you benefit from a bull call spread if the underlying asset will increase in value. The market sentiment should go higher.
Bull + Call = Bull represents a market going higher + Call is an option you buy if you think the market is going to go higher.
The most important element of the bull call spread is the assumption that the market price will rise.
What is the maximum risk associated with spreading bull calls?
The maximum loss you can suffer with a bull call spread is the premium price you pay for the option plus the fees. The potential loss will always be known before trading.
What is the maximum profit you can earn from the call spread trading strategy?
The profit can be calculated by taking the difference of the strike prices (ATM call and ATM call) minus the maximum risk, which we calculated previously.
Call spread option profit = Strike prices – Maximum risk
Let’s look at a quick example so we can apply the theory of options trading.
For this example, we’ll go with Apple’s pricing options.
At the time of writing this Options Spread Strategy PDF, Apple’s stock price is trading around $223 per share.
The first step to setting up your bull call spread is to buy ATM calls at $223. Second, because we assume that the APPL stock price will go higher, we sell ATM calls at 250 dollars. Our winnings will be capped at $250.
For simplicity, let’s assume you pay $2 for the ATM calls and receive $1 for selling the ATM calls. The cost associated with this trade will be only $1 ($2 long call premium – $1 short call profit = $1 x at 100 contract size = $100).
The ultimate cost of $1 is less than just buying out ATM calls, that’s why we have the expression ‘limited risk’.
The right way to buy cheap options is to use the call spread strategy. However, this strategy for trading options is more suitable if you think that the underlying asset will rise only moderately.
In the next segment, we take a box spread strategy and construct a practical example that leads to a risk-free arbitrage opportunity.
Example of a strategy for box distribution (long box)

The box spread is a complicated arbitrage strategy that takes advantage of the price efficiency in option pricing. When the spread options are underpriced relative to their expiration date, a risk-free arbitrage trading opportunity is created.
The strategy for spreading the box is also known as the long box strategy.
Setting up options for the spread of a box involves putting together a strategy for trading with four legs or the combination of two vertical spreads as follows:
- Buy a bull call spread option (1 ITM call and 1 ATM call).
- Buy a bear spread option (1 ITM put and 1 ATM put).
The strategy for the short-case options is opposite to the long-case strategy.

The way you take advantage of the box spread options and create a risk-free position is by using the same expiration dates and strike prices for the vertical spread. While we eliminate the risk, the distribution of the box also has the disadvantage of only providing a small return.
Example of a box spread
Let’s take a simple example of the Alibaba indicator symbol BABA trading at $180. The following option premium prices are available:
- October 175 call – $5
- October 185 call – $1
- October 175 put – $ 50
- October 185 put – $ 5
To execute a subject spread, the investor must buy both vertical spreads:
- Buy Bull Call Spread = Buy October 175 call + Sell October 185 call = ($5 x $100 contract size) – ($1 x $100 contract size) = $400.
- Buy Bear Put Spread = Buy October 175 put + Sell October 185 put = ($1.5 x 100 contract size) – ($5 x $100 contract size) = $350.
Not including commissions, the total cost of opening the subject spread is $400 + $350 = $750.
The maturity value of the distribution of the strike price is: $ 185 – $ 175 = $ 10 x $ 100 shares = $ 1,000.
The total profit without including the option fee is calculated as follows: $1,000 – $750 = $250.
If you use the wrong Options broker, the potential profits generated by the subject spread can be offset by the large commissions. Be sure to invest in options using Robinhood, the commission-free platform.
When Should You Use the Butterfly Spread Option Strategy?

The butterfly spread is a neutral trading strategy that can be used if you expect low volatility in the underlying asset. The butterfly spread uses a combination of a bull spread and a bear spread, but with only three legs. If you are trying to go long, the three-leg option strategy can be constructed as follows:
- Buy in-the-money call
- Sell two at-the-money calls
- Buy one call without money
The butterfly risk for long calls is limited to the premium cost you pay for opening the tripod positions. The butterfly can also be constructed by combining and selling a belt and buying a choke.
Learn the art of trading the straddle option spread strategy to take the next big step: Straddle Option Strategy – Profit from Big Moves.
The short butterfly strategy is the reverse strategy for the long butterfly.
Final words – options distribution strategies
While stock traders need to be 100% right in order to make a profit, the options spread strategies can make you money even if you are only partially right about your trades. Option spreads can help you develop non-directional trading strategies, such as the example of the option spread option strategy outlined in this course on options spreads.
Many options traders begin their career by simply buying puts or calls. But at some point along with the evolution of an options trader, they quickly move to spread trading options. For example, implementing a strategy for spreading bull call options gives you better risk control.
For more options trading tricks and strategies follow: Top 10 Options Blogs and Websites to Follow in 2019.
Do not forget that trading in spread options exists with many alternatives for managing risk. Nowadays, most options trading platforms make it easy to place complex options strategies at once. Try them on a demo options platform before risking your hard-earned money.
Thanks for reading!